zinc stearate
zinc stearate is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
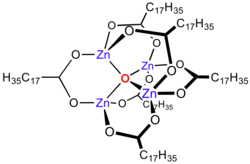
Zinc stearate is a "zinc soap" that is widely used industrially. In this context, soap is used in its formal sense, a metal salt of a fatty acid: in this case stearic acid. It is a white solid that repels water. It is insoluble in polar solvents such as alcohol and ether but soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons (e.g., benzene) and chlorinated hydrocarbons when heated. It is the most powerful mold release agent among all metal soaps. It contains no electrolyte and has a hydrophobic effect. Its main application areas are the plastics and rubber industry, where it is used as a releasing agent and lubricant which can be easily incorporated.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
zinc octadecanoate
| |
| Other names
zinc distearate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.321 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H70O4Zn | |
| Molar mass | 632.33 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | soft, white powder |
| Odor | slight, characteristic |
| Density | 1.095 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 120 to 130 °C (248 to 266 °F; 393 to 403 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility in Ethanol | insoluble |
| Solubility in ether | insoluble |
| Solubility in benzene | slightly soluble |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H335, H400, H413 | |
| P261, P271, P273, P304+P340, P312, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 277 °C (531 °F; 550 K) |
| 420 °C (788 °F; 693 K) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 15 mg/m3 (total) TWA 5 mg/m3 (resp) |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3 (total) TWA 5 mg/m3 (resp) |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Zinc carboxylates, e.g. basic zinc acetate, adopt complex formulas, and are not simply dicarboxylates of zinc. Instead the formula for most zinc carboxylates is Zn4O(O2CR)6, consisting of a Zn4O6+ core with carboxylate ligands spanning the edges.

