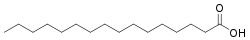
Palmitic acid
Palmitic acid is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms. Its chemical formula is CH3(CH2)14COOH, and its C:D ratio (the total number of carbon atoms to the number of carbon-carbon double bonds) is 16:0. It is a major component of palm oil from the fruit of Elaeis guineensis (oil palms), making up to 44% of total fats. Meats, cheeses, butter, and other dairy products also contain palmitic acid, amounting to 50–60% of total fats.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexadecanoic acid | |
| Other names
Palmitic acid
C16:0 (Lipid numbers) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.284 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 256.430 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Density | 0.852 g/cm3 (25 °C) 0.8527 g/cm3 (62 °C) |
| Melting point | 62.9 °C (145.2 °F; 336.0 K) |
| Boiling point | 351–352 °C (664–666 °F; 624–625 K) 271.5 °C (520.7 °F; 544.6 K), 100 mmHg 215 °C (419 °F; 488 K), 15 mmHg |
| 4.6 mg/L (0 °C) 7.2 mg/L (20 °C) 8.3 mg/L (30 °C) 10 mg/L (45 °C) 12 mg/L (60 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in amyl acetate, alcohol, CCl4, C6H6 Very soluble in CHCl3 |
| Solubility in ethanol | 2 g/100 mL (0 °C) 2.8 g/100 mL (10 °C) 9.2 g/100 mL (20 °C) 31.9 g/100 mL (40 °C) |
| Solubility in methyl acetate | 7.81 g/100 g |
| Solubility in ethyl acetate | 10.7 g/100 g |
| Vapor pressure | 0.051 mPa (25 °C) 1.08 kPa (200 °C) 28.06 kPa (300 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.75 |
| −198.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.43 (70 °C) |
| Viscosity | 7.8 cP (70 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
463.36 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
452.37 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−892 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
10030.6 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 206 °C (403 °F; 479 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Palmitates are the salts and esters of palmitic acid. The palmitate anion is the observed form of palmitic acid at physiologic pH (7.4). Major sources of C16:0 are palm oil, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, and milk fat.