Lidocaine
Lidocaine is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
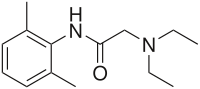
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Lidocaine: /ˈlaɪdəkeɪn/ LY-də-kayn Lignocaine: /ˈlɪɡnəkeɪn/ LIG-nə-kayn |
| Trade names | Xylocaine, others |
| Other names | lignocaine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Local Monograph
Systemic Monograph Ophthalmic Professional Drug Facts |
| MedlinePlus | a682701 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, subcutaneous, topical, by mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 35% (by mouth) 3% (topical) |
| Metabolism | Liver, 90% CYP3A4-mediated |
| Onset of action | Within 1.5 min (IV) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 h to 2 h |
| Duration of action | 10 min to 20 min (IV), 0.5 h to 3 h (local) |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.821 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 234.343 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 68 °C (154 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
If injected intravenously, it may cause cerebral effects such as confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate. There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy. A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems. It is generally safe to use in those allergic to tetracaine or benzocaine. Lidocaine is an antiarrhythmic medication of the class Ib type. This means it works by blocking sodium channels thus decreasing the rate of contractions of the heart. When injected near nerves, the nerves cannot conduct signals to or from the brain.
Lidocaine was discovered in 1946 and went on sale in 1948. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 262nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.

