Gum arabic
Gum arabic is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (November 2022) |
Gum arabic (gum acacia, gum sudani, Senegal gum and by other names) (Arabic: صمغ عربي) is a tree gum exuded by two species of Acacia sensu lato, Senegalia senegal and Vachellia seyal. However, the term "gum arabic" does not actually indicate a particular botanical source. The gum is harvested commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan (about 70% of the global supply) and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia. The name "gum Arabic" (al-samgh al-'arabi) was used in the Middle East at least as early as the 9th century. Gum arabic first found its way to Europe via Arabic ports, and retained its name of origin.

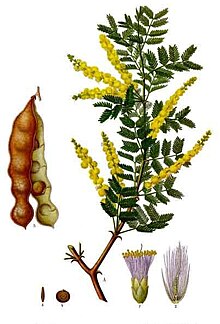
Gum arabic is a complex mixture of glycoproteins and polysaccharides, predominantly polymers of arabinose and galactose. It is soluble in water, edible, and used primarily in the food industry and soft-drink industry as a stabilizer, with E number E414 (I414 in the US). Gum arabic is a key ingredient in traditional lithography and is used in printing, paints, glues, cosmetics, and various industrial applications, including viscosity control in inks and in textile industries, though less expensive materials compete with it for many of these roles.[citation needed]

