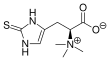
Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid and is a thiourea derivative of histidine, containing a sulfur atom on the imidazole ring. This compound occurs in relatively few organisms, notably actinomycetota, cyanobacteria, and certain fungi. Ergothioneine was discovered by Charles Tanret in 1909 and named after the ergot fungus from which it was first purified, with its structure being determined in 1911.
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-3-(2-Sulfanylidene-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-2-(trimethylazaniumyl)propanoate | |||
| Other names
L-Ergothioneine; (+)-Ergothioneine; Thiasine; Sympectothion; Ergothionine; Erythrothioneine; Thiolhistidinebetaine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.131 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H15N3O2S | |||
| Molar mass | 229.30 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Melting point | 275 to 277 °C (527 to 531 °F; 548 to 550 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
In humans, ergothioneine is acquired exclusively through the diet and accumulates in erythrocytes, bone marrow, liver, kidney, seminal fluid, and eyes. Although the effect of ergothioneine in vivo is under preliminary research, its physiological role in humans is unknown. Ergothioneine is sold as a dietary supplement.