DMAE
Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) is an organic compound known for its skin-firming and anti-aging properties. Naturally found in small amounts in the human body and certain fish like salmon and sardines, DMAE is widely used in skincare for its ability to improve skin elasticity, reduce fine lines, and promote a more lifted appearance.
One of DMAE’s primary functions is to enhance muscle tone by stabilizing cell membranes and reducing oxidative stress. This leads to a temporary tightening effect, making the skin appear firmer and more contoured. Additionally, its antioxidant properties help protect the skin from free radical damage, slowing down the signs of aging.
DMAE is commonly found in serums, creams, and anti-aging formulations designed to improve skin firmness and texture. While it provides noticeable short-term lifting effects, long-term use may also contribute to overall skin resilience and smoothness. Some individuals may experience mild irritation or tingling when first using DMAE, so it is often recommended to start with lower concentrations and gradually increase usage.
Due to its ability to promote a youthful, toned appearance, DMAE is a popular ingredient in skincare products aimed at mature skin, particularly those targeting sagging and loss of firmness.
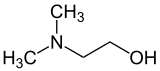
Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE or DMEA) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2OH. It is bifunctional, containing both a tertiary amine and primary alcohol functional groups. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is used in skin care products for improving skin tone and also taken orally as a nootropic. It is prepared by the ethoxylation of dimethylamine.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Dimethylamino)ethan-1-ol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DMAE, DMEA |
| 1209235 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.221 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Deanol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2051 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 89.138 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 890 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −59.00 °C; −74.20 °F; 214.15 K |
| Boiling point | 134.1 °C; 273.3 °F; 407.2 K |
| log P | −0.25 |
| Vapor pressure | 816 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.23 (at 20 °C) |
| Basicity (pKb) | 4.77 (at 20 °C) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4294 |
| Pharmacology | |
| N06BX04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| Flash point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.4–12.2% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
|
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanols
|
|
Related compounds
|
Diethylhydroxylamine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

