Dimethicone
Dimethicone is a class of synthetic polymers used in skincare and haircare products to enhance texture, improve spreadability, and create a protective barrier on the skin or hair. Silicone-based ingredients, such as dimethicone and cyclopentasiloxane, provide a silky-smooth finish, reduce friction, and help lock in moisture. Despite misconceptions, silicones do not clog pores when properly formulated, and they are widely used in primers, foundations, and serums to create a long-lasting, flawless effect.
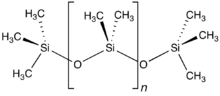
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), also known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer with a wide variety of uses, from cosmetics to industrial lubrication and passive daytime radiative cooling.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
poly(dimethylsiloxane)
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.442 |
| E number | E900 (glazing agents, ...) |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3[Si(CH3)2O]nSi(CH3)3 | |
| Density | 0.965 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | N/A, vitrifies |
| Boiling point | N/A, vitrifies |
| Pharmacology | |
| P03AX05 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
PDMS is particularly known for its unusual rheological (or flow) properties. It is optically clear and, in general, inert, non-toxic, and non-flammable. It is one of several types of silicone oil (polymerized siloxane). The applications of PDMS range from contact lenses and medical devices to elastomers; it is also present in shampoos (as it makes hair shiny and slippery), food (antifoaming agent), caulk, lubricants and heat-resistant tiles.




