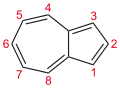
Azulene
Azulene is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
Azulene is an aromatic organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Naphthalene is colourless, whereas azulene is dark blue. The compound is named after its colour, as "azul" is Spanish for blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Azulene | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Bicyclo[5.3.0]decapentaene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.449 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 128.174 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 99 to 100 °C (210 to 212 °F; 372 to 373 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 242 °C (468 °F; 515 K) | ||
| -98.5·10−6 cm3/mol
g/L | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−1266.5 kcal/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Azulene has a long history, dating back to the 15th century as the azure-blue chromophore obtained by steam distillation of German chamomile. The chromophore was discovered in yarrow and wormwood and named in 1863 by Septimus Piesse. Its structure was first reported by Lavoslav Ružička, followed by its organic synthesis in 1937 by Placidus Plattner.