Sodium polyaspartate
Sodium polyaspartate is a widely used ingredient in cosmetics, personal care, and skincare formulations. Depending on its function, it may serve as a moisturizer, preservative, emulsifier, or active ingredient to enhance the overall effectiveness and performance of a product.
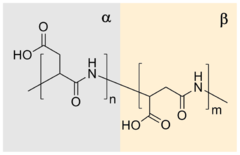
Polyaspartic acid (PASA) is a biodegradable, water-soluble condensation polymer based on the amino acid aspartic acid. It is a biodegradable replacement for water softeners and related applications. PASA can be chemically crosslinked with a wide variety of methods to yield PASA hydrogels. The resulting hydrogels are pH-sensitive such that under acidic conditions, they shrink, while the swelling capacity increases under alkaline conditions.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PASP
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| ChemSpider |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| (C4H5NO3)n | |
| Molar mass | variable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Sodium polyaspartate is a sodium salt of polyaspartic acid.
In nature, PASA has been found in as fragments of larger proteins with length up to 50 amino acids, but as of 2004 had not been isolated as a pure homo polymeric material from any natural source. The first isolation of synthetic oligomeric sodium polyaspartate, obtained by thermal polycondensation of aspartic acid, was reported by Hugo Schiff in late 19th century. Later it was proposed that thermal polymerization process leads through polysuccinimide intermediate. Polyaspartic acid is produced industrially in both the acid form and as the sodium salt.

